Robotics is such an exciting and growing field. Many people want to learn how to make robots, but sometimes it is hard to know where to start.
If you are starting from scratch, or if you already know some electronics and programming concepts, learning robotics with Arduino is a good idea. It will give you some good basics that you can use later to build larger robotics projects.
Niryo One is an example of a robot powered by Arduino. Great things can be accomplished with Arduino ! You’ll also find more examples of robotics applications on Instructables, an amazing website with some open source tutorials.
In this post we’ll show you an overview and some guidelines, about where to start, which board, sensors, motors to use, and what to focus on.
What you can do, and what you can’t do with an Arduino board
An Arduino board is composed of a microcontroller, some LEDs, a reset button, and many pins that you can use for input/output operations.
With so many pins available, you can easily read data from sensors, or control different motors and actuators. That is what makes Arduino great for learning robotics. It’s kind of an all-in-one tool to interface all the hardware you need to control.
But don’t think about artificial intelligence, 3D visualization and other heavy algorithms. Microcontrollers are not powerful enough, and it is not the purpose of using an Arduino board. Arduino is mostly used to do input/output operations, and small computations.
Don’t worry though, you can still do amazing stuff with just an Arduino board and a few motors and sensors ! There are more than enough resources to learn robotics with Arduino.
And then, if you want to learn deeper robotics concepts and add an intelligence layer to make your system more clever, you can just control your Arduino board from another computer (like a Raspberry Pi board), there are many easy ways to do that.
Choosing an Arduino board
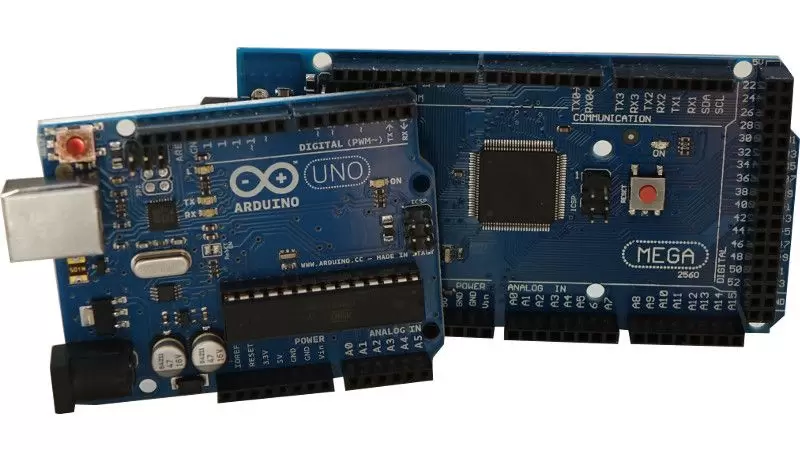
First of all you have to choose which Arduino board is best suited for your robotics project. Our recommendation : starting with a Uno or a Mega is just fine.
The Uno has an ATmega328P microcontroller and the Mega has an ATmega2560. Their CPU is both clocked at 16 MHz. Uno has 2ko of SRAM while Mega has 8ko. That’s pretty small, so think twice before creating huge arrays of variables.
Then, the biggest difference is the interface with hardware components. Uno has 14/6 digital input/output pins while Mega has 54/15. That’s why Arduino Mega is preferred for bigger projects, as you can plug more hardware.
And if you like 3D printing, you may know that some shields were created just for the Arduino Mega board, like RAMPS 1.4 shield, which allows you to use 5 stepper motors and power them from an external power source.
RAMPS 1.4 shield on top of an Arduino Mega board
At Niryo we are definitely fan of the Arduino Mega + RAMPS 1.4 combination, that we use to power our robot !
So, if you want to learn only the basics, get an Arduino Uno, otherwise we advise you to directly start with a Mega. More Arduino boards are available for different robotics applications. For a very smaller board check out Arduino Nano. If you want ethernet connectivity then Arduino Yun is for you, and fore more advanced calculation you may choose the Arduino Due.
Installing the IDE
The first step is to install the software (IDE) which will allow you to write and upload the code on your Arduino board. You can download the Arduino IDE on the official Arduino website. There is a version for Windows, Mac OS and Linux : everyone’s happy.
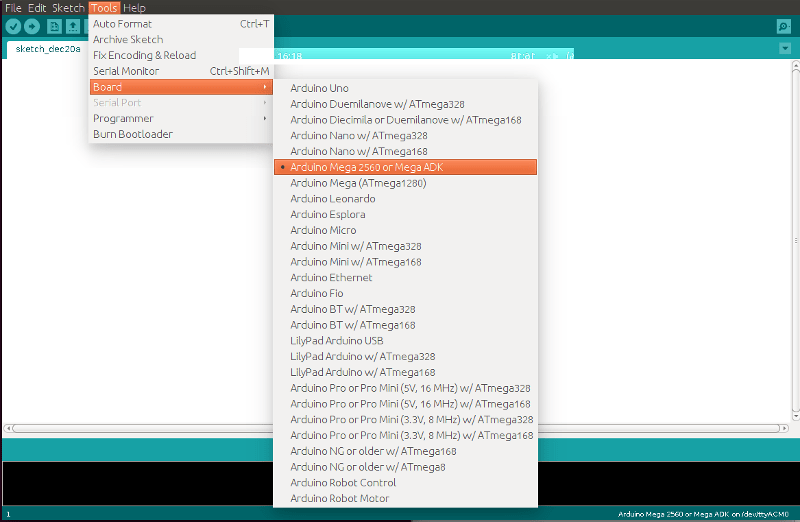
Once you installed the IDE, you need to plug your Arduino board to your computer with the USB wire. Normally, the IDE should automatically recognize the USB port where the Arduino board is plugged. You just need one extra step : go in “Tools”->”Board” and select the Arduino board you are using.
Then all you have to do is write your code and upload it ! If you are not familiar with Arduino programming, have a look in File->Examples. Many examples using standard Arduino libraries can be found here. It will get you up to speed easily. Now you’re ready to learn robotics with Arduino !
Controlling motors (output)
As we saw, an Arduino board will be used as an input/output platform. In this post we are focusing on robotics applications. So… What do you need to move a robot ? Yep, motors.
Two kinds of motors can be easily controlled by Arduino : servo motors and stepper motors.
Servo motors
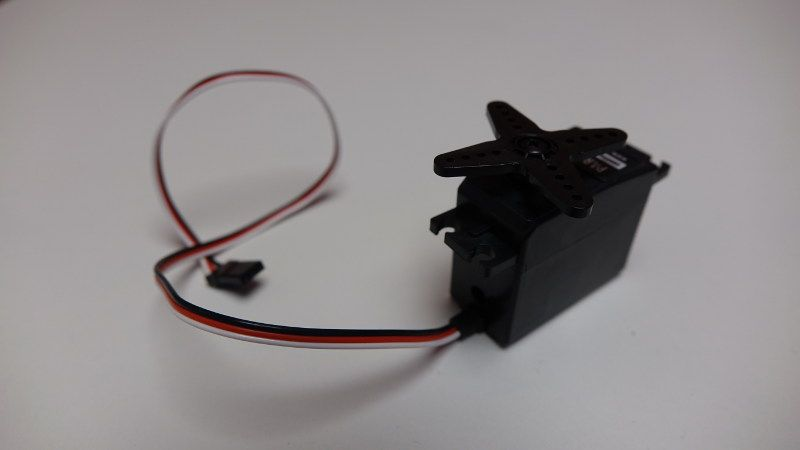

Servo motors just need a 3 wires connector and can be directly plugged to the Arduino board. Standard hobby servos can move between 0 and 180°. You can control a servo with the Arduino Servo library. Some examples are provided on the Arduino website.
Basically, how you control a servo motor is by giving it the value of the goal angle. It will automatically go to this angle. You can adjust the speed by incrementing the goal over different periods of time.
You can also read the value of the current angle. Servos give you feedback which is very useful. But, be aware that most hobby servos have a 180° range, which can be a problem in some applications (you can find some alternative servos on the Internet, each with its pros and cons).
A classic hobby servo motor with a 3 wires connector
Stepper motors
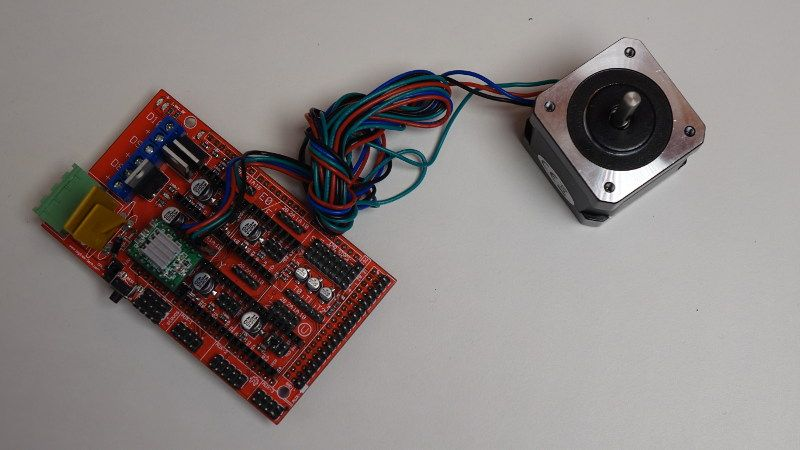
Stepper motors are different. You can’t directly plug them to the Arduino board. You need another linked card, or a shield like RAMPS 1.4 for the Mega board. That’s why we prefer Arduino Mega + RAMPS 1.4 for stepper motors, as it gives an easier and nicer interface.
For controlling a stepper motor, you need to tell it to do one step. That’s pretty much it. So, you need to know how many steps you can do for a 360° move. Then, by adding or removing delay between each step, you can reduce or increase the speed of the motor. You can find examples on the Arduino website. A stepper motor will generally run more smoothly than a servo motor, and it has infinite rotation.
Stepper motor plugged to RAMPS 1.4 shield, with a motor driver
However you don’t have feedback from a stepper motor. So if your robot needs to be aware of the current angle you will have to add an encoder or a sensor to know if the stepper missed some steps due to a too high torque.
After you learn how to deal with servo and stepper motors, you will be able to choose which one is best suited for your robot. And there are more kind of motors out there…
Reading data from sensors (input)
Once you’ve managed to control your motors, you may want to make your robot adapt its behaviour to environment changes.
There are tons of sensors you can use with an Arduino board :
- Optical distance measurement
- Laser detector
- Accelerometer
- Gyroscope
- Magnetometer
- RFID reader
- Thermometer
- Load sensor
- Force sensor
- …
Imagine all the robotics applications you can do with all those sensors ! You can easily find libraries, tutorials and datasheets online to learn how to read and analyze data. Mostly data acquisition will be done via serial, i2c and spi communication.
For example, you could use an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) to control the inclination of your robot. An IMU is composed of different sensors : accelerometers, gyroscope and magnetometer (optional). Then, if you want your robot to detect and avoid collisions with objects and people, you can add a laser detector.
All of that just with your Arduino board. Robotics hardware has now become nice and user-friendly !
Logging
When you upload your code on the Arduino board, you don’t know what is exactly happening when the program runs. Maybe you will see some weird behaviors or your robot might just not do anything.
The easiest way to debug or to display some state in your program is to use the Serial library. All you need to do is to write Serial.print(), and to open the serial monitor on the Arduino IDE. That way you will be able to see logs, and to send manual commands via serial communication for debugging. (If you see some weird printed characters, be sure that the baud rate is the same on Arduino and the serial monitor)
Time for you to learn robotics with Arduino !
We gave here an overview of what you can do to learn robotics with Arduino boards. If you are struggling with some parts, don’t worry too much as there is an active online community around Arduino boards and projects.
We hope this post will be useful for you, so you can get more into robotics, learn new things, and share your projects with robotics communities.
And if you are interested in learning robotics with Arduino on a cool and useful project, you will definitely like Niryo One !