According to UNESCO, by 2030, more than 80% of jobs will require STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) skills. This statistic highlights the crucial importance of these disciplines in the modern world.
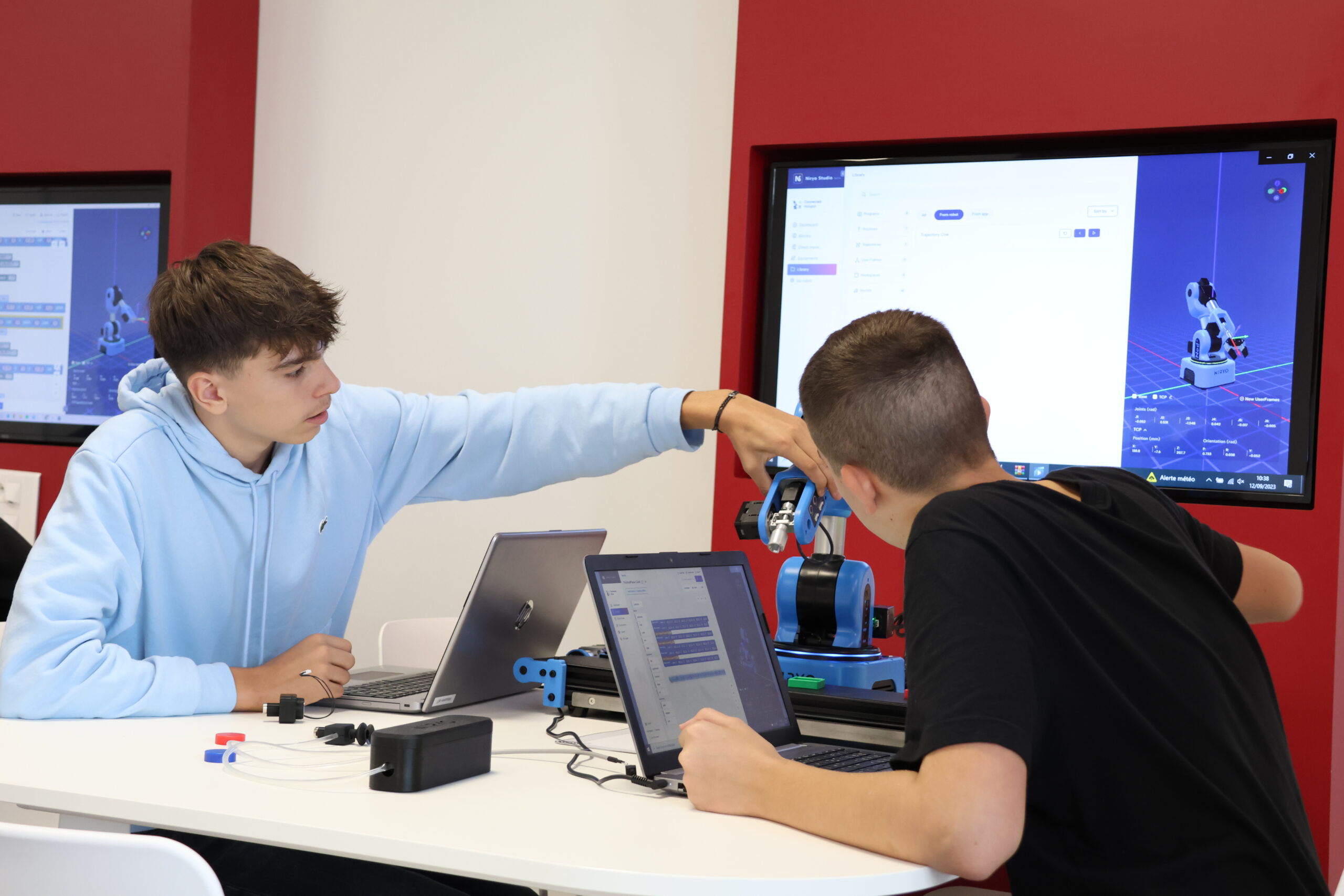
Educational robots, such as Lego robots or Thymio, are innovative tools that allow young people to learn STEM in a fun and interactive way. They provide a practical application of theoretical concepts, making understanding and memorization easier. Traditional STEM teaching is often perceived as abstract and disengaging. Educational robots provide a solution to this problem by turning learning into a hands-on, collaborative experience.
In France, an increasing number of schools are integrating robotics into their curriculum, recognizing the potential of these tools to develop students’ critical thinking and creativity. Robots are no longer just automation tools in industry but also essential educational tools to prepare the next generation for tomorrow’s technological challenges.
The benefits of educational robots in STEM learning
The integration of educational robots into school curricula represents a major breakthrough that is radically changing the way young people approach STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) disciplines. Educational robotics offers a multitude of benefits, from increased student engagement to the development of essential skills for the future.
Interactive and fun learning
Robots make learning more engaging by transforming abstract concepts into concrete, interactive experiences. The playful aspect, or “gamification,” is crucial: it stimulates students’ curiosity and motivation, encouraging them to explore and experiment.
Robots like Thymio, for example, allow young people to instantly visualize the effects of their code programs, making robotics learning fun and accessible.
Development of practical skills
Programming and robotics are increasingly sought-after skills in the professional world. Educational robots provide an ideal platform for learning these skills. By manipulating and programming robots, students develop problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and teamwork abilities. Collaboration around robotic projects, such as building Lego robots, also fosters idea exchange and knowledge sharing.
Adaptation to different learning levels
One of the major strengths of educational robots is their ability to adapt to all learning levels. From simple robots for children to more complex solutions for advanced students, there is a wide range of robotic equipment suited for every stage of learning. Personalized learning is also possible with applications and software that allow the creation of tailored activities.
Different types of educational robots and their applications
Educational robotics offers a multitude of solutions to learn in a fun and interactive way. Educational robots come in various categories, each with specific applications.
Programming robots
These programming robots, such as Thymio or mBot, are designed to introduce young people to programming and algorithms. They help visualize basic coding concepts like loops and conditions. It’s an excellent tool for developing logical thinking and problem-solving skills.
In France, many courses and workshops use these robots to familiarize young people with automation.
Construction robots
LEGO Mindstorms and VEX Robotics are examples of construction robots. They allow young people to learn about engineering, design and mechanics. By building and programming their own robots, they develop their creativity and innovative spirit.
These solutions are often used in the classroom for group projects, encouraging collaboration and teamwork. Handling this equipment helps students understand the entire robotic system.
Robots for learning math and science
Some robots are designed specifically for learning math and science. Educational robotics can simulate scientific experiments to visualize abstract concepts.
For example, educational robots can reproduce the motion of planets or illustrate a chemical reaction. They make learning more concrete and interactive, stimulating young people’s curiosity and interest in science. These robots can also be used to perform precise measurements, helping students to better understand and analyze scientific data.
In industry, these robots are also used for similar tasks, demonstrating their practical application in the real world. In addition, the use of these robots facilitates the storage and analysis of information related to scientific experiments, thus optimizing their use.
The impact of educational robotics on the future of STEM education
The field of educational robotics represents a significant advancement in the way young people approach STEM disciplines. The integration of robots into classrooms transforms learning into an interactive and hands-on experience, thus preparing students for the challenges of the future.
Preparing for tomorrow’s professions
The importance of STEM skills in the labor market is undeniable. Companies, both in France and globally, are seeking individuals who can master technological tools and propose innovative solutions. Educational robots, such as Lego kits or Thymio, enable students to learn the basics of programming, automation, and design—skills that are essential for the careers of tomorrow.
Inclusion and equal opportunities
One of the great benefits of educational robots is their ability to make STEM education accessible to all. By providing adapted applications and courses, these tools can help address inequalities in access to education, particularly for students from disadvantaged backgrounds or with disabilities.
Challenges and prospects
Despite their many benefits, educational robots face challenges such as equipment cost and accessibility. In addition, teacher training in the use of these systems is crucial to ensure effective integration into the classroom.
However, the future of educational robots looks promising. With increasingly sophisticated and personalized solutions, these technologies are paving the way for a new era in STEM education.