Industry 4.0, also called industry of the future, is a new way of understanding, designing and organizing production tools.
A constantly evolving industry
The industry has evolved greatly since its inception. Today, it is experiencing and will continue to experience many major developments, since the entire industrial sector is changing as technologies evolve, developing and becoming more and more integrated into the heart of industrial processes.
These profound modifications and additions of new technologies are disrupting the habits and organizations of industrialists. This major technological breakthrough offers an extraordinary field of innovation, progress and growth. Thus, if Industry 4.0 is becoming the essential reference for industrial production, it is still complex for many players to understand and requires some explanation, since it impacts many aspects of the industry with a process orientation: design, control, manufacturing, service, work organization…
What does Industry 4.0 provide?
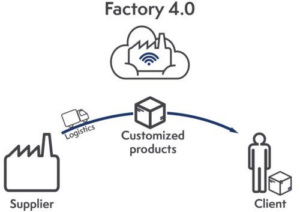
Industry 4.0, with its technological contributions, is a major challenge to meet the new needs of consumers who are becoming more and more demanding (short circuits, organic farming, vegan products, extreme seasonality, etc.) while mass production has always involved a certain inertia to change due to the investments required both in terms of financial resources and time, to establish a production process. This inertia can now be avoided by easily and quickly adapting production to customer needs, allowing customization to be taken to the extreme. Thus, Industry 4.0 pushes back the limits of traditional industry and allows manufacturers to be customer-centric.
Technologies involved in Industry 4.0
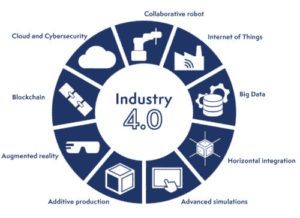
It is notably thanks to the appearance of nine new technological bricks that Industry 4.0 takes on its full meaning:
- Collaborative robots
- Cloud and Cybersecurity
- Blockchain
- Augmented reality
- Additive production
- Advanced simulations
- Horizontal integration
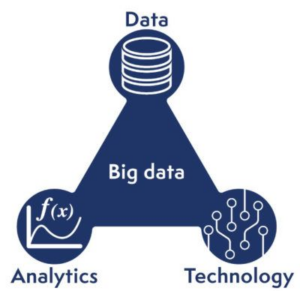
- Big data
- Industrial Internet / IoT (5G)
Data at the heart of Industry 4.0
This data is indeed a crucial element since, without it, no metric can be generated. It is thus necessary to enter on a system in 3 times:
COLLECT
Using sensors and IoT
ANALYZE
Process information
EXPLOIT
Structure information and bring out concrete levers allowing decision-making
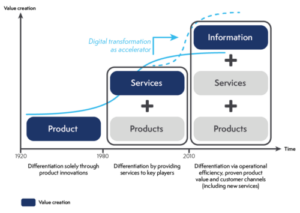
Industry 4.0 uses data to generate value, and this goes beyond product value, since this value creation affects products as much as services and information.
What process improvements makes Industry 4.0?
Thus, the data, the information, collected, allows to derive this information allows to derive on 5 process improvements:
- Design process
- Monitoring
- Production/Continuous improvement
- Maintenance
- Personal organization
Industry 4.0: why now?
Technological convergence
Technological advances, both hardware and software, the interconnectivity of machines and their connection to the Internet, are disrupting factory operations. Indeed, they allow manufacturers to reinvent themselves in order to develop their activities, take market share and conquer new ones.
Market convergence
Markets, their supply and demand curves, are changing rapidly. Customers want unique, personalized products that meet increasingly specific needs.
This constant evolution of the markets is pushing manufacturers to review their business models, since there is no longer any question of mass production for a single product. However, manufacturers must profit from their products, meet shareholders’ expectations, while remaining competitive in the face of ever more intense competition. This situation implies many challenges to be overcome when we have to produce an increasingly wide range of products with products with shorter and shorter life cycles.
Meeting these new challenges using models designed for needs that no longer correspond to those of today is not possible. The many strengths of the industry 4.0 model allow it to meet these challenges since it allows companies to gain flexibility, agility and responsiveness.
What are the benefits of Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 brings many benefits to manufacturers, both defensive and offensive. The defensive benefits allow in particular to adapt its productive tool to heavy structural trends such as the aging of the working population, when the offensive benefits concern the optimization of production units to make them as competitive as possible.
Industry 4.0 will notably allow:
- To adapt the productive tool according to the needs and the aging of the population,
- Optimize the consumption of energy and raw materials,
- Increase agility
- Increase responsiveness,
- Increase the flexibility of production,
- Improve the reliability of machines,
- Optimize human, material and energy resources,
- To strengthen the processing industry,
- To better serve customers through flexibility and product customization,
- To forge a strong bond with customers,
- To maintain and develop future industrial jobs.
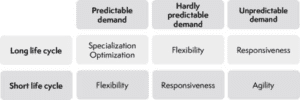
Flexibility, responsiveness and agility are three terms that evoke the same meaning but are actually quite distinct:
- Flexibility is the ability to respond to various customer demands,
- Responsiveness is the speed of satisfaction of unanticipated requests,
- Agility is the company’s ability to reconfigure itself according to changes in its environment, its market.
Depending on its “environment”, a company must adapt its organization and its “response”:
The majority of current production tools show excellent results in meeting foreseeable demand. The systems are however very specialized and require long deployment times. However, to meet an unpredictable demand with increasingly shorter product life cycles, new tools are essential to meet market expectations.
It is in this market evolution that Industry 4.0 takes on its full meaning, since it brings the necessary agility to manufacturers, to the point of making it possible to modify manufacturing processes in one click.
Industry 4.0: future evolutions
Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT for Internet of Things) are having effects on the machines themselves: they are becoming more and more autonomous, mobile and easier to control. Soon the robots will be smart enough to understand our language and our gestures. Thus, if today collaborative robots are tools for production operators, they are also becoming assistants of choice since their characteristics, in particular their precision and speed, give humans new capabilities.